This Village-Made Chinese Pain Reliever Eliminates Back And Joint Pain!
Arthritis in Shoulder Joint: Surgical vs. Non-Surgical Treatments
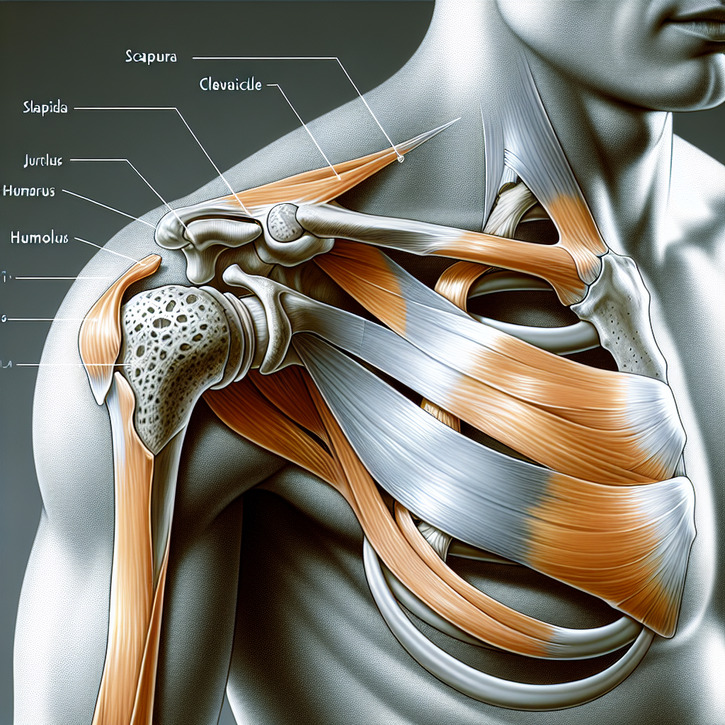
Introduction to Arthritis in Shoulder Joint
Arthritis in the shoulder joint is a condition that affects many individuals, particularly as they age. It involves the inflammation and degeneration of the shoulder joint, leading to pain and decreased mobility. Understanding the various treatment options available is crucial for managing this condition effectively. This blog post will discuss the differences between surgical and non-surgical treatments for shoulder arthritis, providing insights into their effectiveness, risks, and benefits.
Understanding Shoulder Arthritis
Shoulder arthritis typically occurs when the cartilage that cushions the bones in the shoulder joint wears down over time. This degeneration can lead to pain, swelling, and stiffness, making it difficult to perform daily activities. There are several types of shoulder arthritis, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and post-traumatic arthritis, each with its own causes and symptoms.
Prevalence and Risk Factors
Arthritis in the shoulder joint is more common in older adults, but it can also affect younger individuals, particularly those with a history of shoulder injuries. Risk factors include age, genetics, previous shoulder injuries, and certain occupations or activities that put repetitive stress on the shoulder. Understanding these risk factors can help individuals take preventive measures to reduce their risk of developing shoulder arthritis.
Importance of Early Diagnosis
Early diagnosis of shoulder arthritis is crucial for effective management and treatment. Identifying the condition in its early stages can help prevent further joint damage and improve the quality of life for individuals affected. Regular check-ups and consultations with healthcare professionals can aid in the early detection of shoulder arthritis, allowing for timely intervention.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Arthritis in Shoulder Joint
Common Symptoms
Common symptoms of shoulder arthritis include persistent pain, stiffness, and a reduced range of motion in the shoulder joint. Individuals may also experience swelling, tenderness, and a grinding or clicking sensation when moving the shoulder. These symptoms can vary in severity, with some individuals experiencing mild discomfort while others may have debilitating pain.
Diagnostic Imaging Techniques
Diagnostic imaging techniques, such as X-rays, MRI, and CT scans, are essential tools for diagnosing shoulder arthritis. These imaging methods provide detailed views of the shoulder joint, allowing healthcare professionals to assess the extent of cartilage damage and identify any bone spurs or other abnormalities. Accurate imaging is crucial for developing an effective treatment plan.
Clinical Evaluation Methods
In addition to imaging techniques, clinical evaluation methods are used to diagnose shoulder arthritis. These may include physical examinations, range of motion tests, and assessments of the shoulder's strength and stability. Healthcare professionals may also review the patient's medical history and ask about any previous injuries or conditions that could contribute to shoulder arthritis.
Non-Surgical Treatments for Arthritis in Shoulder Joint
Physical Therapy and Exercises
Physical therapy and exercises are often recommended as the first line of treatment for shoulder arthritis. A physical therapist can design a personalized exercise program to improve shoulder strength, flexibility, and range of motion. These exercises can help reduce pain and prevent further joint degeneration, allowing individuals to maintain an active lifestyle.
Medications and Pain Management
Medications and pain management strategies are commonly used to alleviate the symptoms of shoulder arthritis. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce pain and inflammation, while corticosteroids may be prescribed for more severe cases. Pain management techniques, such as heat and cold therapy, can also provide relief for individuals with shoulder arthritis.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications are essential for managing shoulder arthritis and preventing further joint damage. This may include avoiding activities that put excessive stress on the shoulder, maintaining a healthy weight, and incorporating joint-friendly exercises into daily routines. Making these changes can help reduce pain and improve the overall quality of life for individuals with shoulder arthritis.
Advanced Non-Surgical Options
Steroid Injections
Steroid injections are a common non-surgical treatment for shoulder arthritis. These injections deliver corticosteroids directly into the shoulder joint, reducing inflammation and providing pain relief. While steroid injections can be effective, they are typically used as a short-term solution and may need to be repeated periodically for continued relief.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy is an advanced non-surgical treatment option for shoulder arthritis. PRP therapy involves injecting a concentration of the patient's own platelets into the shoulder joint to promote healing and reduce inflammation. This treatment has shown promise in reducing pain and improving joint function, although more research is needed to determine its long-term effectiveness.
Hyaluronic Acid Injections
Hyaluronic acid injections are another advanced non-surgical treatment for shoulder arthritis. These injections provide lubrication to the shoulder joint, reducing friction and improving mobility. Hyaluronic acid injections can help alleviate pain and improve the range of motion in individuals with shoulder arthritis, making it easier to perform daily activities.
Surgical Treatments for Arthritis in Shoulder Joint
Arthroscopy
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to treat shoulder arthritis. During arthroscopy, a small camera is inserted into the shoulder joint, allowing the surgeon to view and repair damaged tissues. This procedure can help relieve pain and improve joint function, with a shorter recovery time compared to traditional open surgery.
Shoulder Joint Replacement
Shoulder joint replacement, also known as shoulder arthroplasty, is a surgical option for severe cases of shoulder arthritis. This procedure involves replacing the damaged shoulder joint with an artificial implant. Shoulder joint replacement can provide significant pain relief and improve mobility, although it requires a longer recovery period and rehabilitation.
Resection Arthroplasty
Resection arthroplasty is a surgical procedure that involves removing a portion of the shoulder joint to relieve pain and improve function. This procedure is typically reserved for individuals with severe shoulder arthritis who have not responded to other treatments. Resection arthroplasty can provide long-term relief, although it may result in reduced joint stability and strength.
Evaluating Surgical vs. Non-Surgical Treatments
Effectiveness and Outcomes
When evaluating surgical vs. non-surgical treatments for shoulder arthritis, it is important to consider the effectiveness and outcomes of each option. Non-surgical treatments can provide significant pain relief and improve joint function, particularly in the early stages of arthritis. Surgical treatments, on the other hand, may offer more substantial relief for individuals with severe joint damage.
Recovery Time and Rehabilitation
Recovery time and rehabilitation are important factors to consider when choosing between surgical and non-surgical treatments for shoulder arthritis. Non-surgical treatments typically have shorter recovery times and may require less intensive rehabilitation. Surgical treatments, however, often involve longer recovery periods and more extensive rehabilitation to restore joint function and strength.
Risks and Complications
Both surgical and non-surgical treatments for shoulder arthritis come with their own risks and potential complications. Non-surgical treatments may have fewer risks, but they may not provide long-term relief for individuals with severe arthritis. Surgical treatments, while potentially more effective, carry risks such as infection, blood clots, and complications related to anesthesia.
Case Studies and Patient Testimonials
Success Stories with Non-Surgical Treatments
Many individuals have experienced success with non-surgical treatments for shoulder arthritis. For example, John, a 62-year-old retiree, found significant relief through physical therapy and hyaluronic acid injections. These treatments helped him regain mobility and reduce pain, allowing him to enjoy his favorite activities without the need for surgery.
Experiences with Surgical Interventions
Surgical interventions have also provided positive outcomes for individuals with severe shoulder arthritis. Sarah, a 55-year-old office worker, underwent shoulder joint replacement after years of debilitating pain. The surgery significantly improved her quality of life, allowing her to return to work and participate in activities she had previously avoided.
Professional Opinions from Orthopedic Specialists
Orthopedic specialists emphasize the importance of individualized treatment plans for shoulder arthritis. Dr. Smith, a renowned orthopedic surgeon, recommends considering both surgical and non-surgical options based on the patient's specific condition and needs. He highlights the importance of early diagnosis and a comprehensive approach to treatment for the best outcomes.
Conclusion and Recommendations
Summary of Treatment Options
In summary, there are various treatment options available for managing arthritis in the shoulder joint. Non-surgical treatments, such as physical therapy, medications, and advanced injections, can provide significant relief for many individuals. Surgical options, including arthroscopy, shoulder joint replacement, and resection arthroplasty, are available for those with severe arthritis or who have not responded to non-surgical treatments.
Factors to Consider in Decision Making
When deciding between surgical and non-surgical treatments for shoulder arthritis, it is important to consider factors such as the severity of the condition, the patient's overall health, and their lifestyle and activity level. Consulting with healthcare professionals and considering their recommendations can help individuals make informed decisions about their treatment options.
Encouraging Regular Follow-ups
Regular follow-ups with healthcare professionals are essential for managing shoulder arthritis effectively. These appointments allow for the monitoring of the condition's progression and the adjustment of treatment plans as needed. Staying proactive and maintaining open communication with healthcare providers can help individuals achieve the best possible outcomes and maintain their quality of life.








